Table of Contents
Introduction
Best Practices for SharePoint Security Management
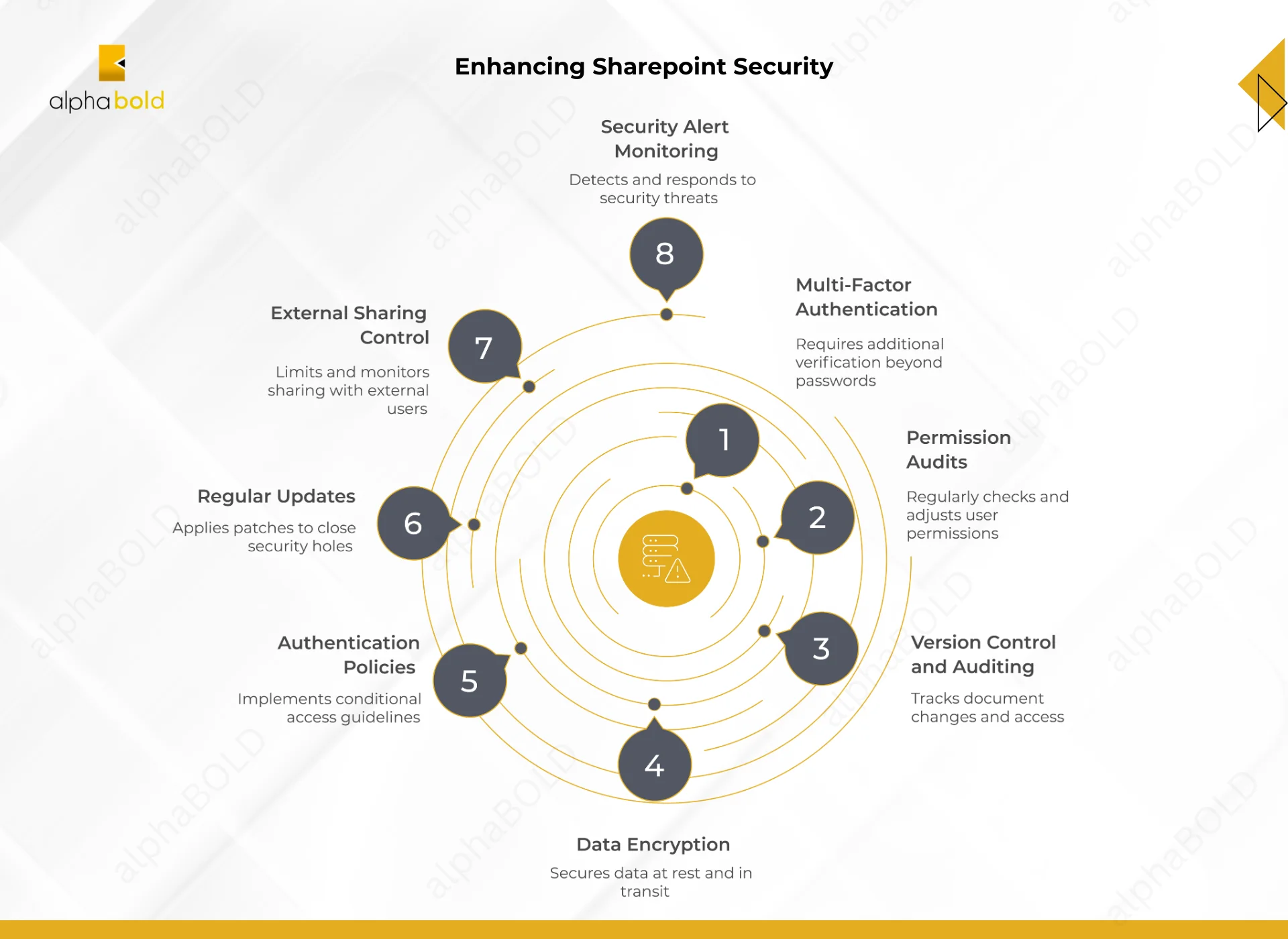
The following are the practices recommended for ease of security handling in Microsoft SharePoint security:
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
MFA enhances security by requiring identity verification beyond just a password—for example, a mobile code. This extra layer of control prevents unauthorized access and protects sensitive data.
Best Practice: Always deploy MFA for every account, particularly for administrators and those who may encounter sensitive data. Given SharePoint’s integration with Microsoft 365, enabling MFA is straightforward—and essential to minimizing risk.
2. Check Permissions Periodically:
Users and teams often inherit unnecessary authorizations, leading to an extensive amount of random data.
Best Practice: Conduct regular permission audits and apply the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP). Use authentication levels and groups to manage access efficiently within your SharePoint environment.
Enhance Your SharePoint Security Management
Protect your data with strong access control, encryption, and monitoring strategies with AlphaBOLD as your partner.
Request a Consultation3. Enable Version Control and Document Auditing
Keeping track of document changes and access can help identify unauthorized modifications and maintain a secure audit trail in case of a security incident. A 2022 study by McAfee found that 82% of organizations experienced accidental data exposure due to misconfigured cloud settings.
Best Practice: Enable versioning in the document libraries to ensure that the versions are created against the changes made in the document. Also, activate auditing to monitor different actions, such as who accessed the documents, modified them, and deleted them. This provides valuable insight into security incidents or compliance audits.
Further Reading: Benefits of Professional SharePoint Migration Services
4. Data Encryption:
Encryption secures data both at rest and in transit, preventing interception or unauthorized access.
Best Practice: Ensure all SharePoint data is protected using strong encryption standards. Microsoft SharePoint security automatically encrypts data at rest, but it’s important to confirm that encryption is correctly configured for your environment. For data in transit, use secure protocols such as TLS or SSL.
5. Implementing Strong Authentication Policies:
Well-defined authentication policies limit exposure to unauthorized users.
Best Practice: In addition to implementing MFA, conditional access guidelines should be implemented based on user location, device, and risk level. Use Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) to manage these guidelines and ensure they are closely integrated into Microsoft SharePoint security measures.
6. Keep SharePoint Updated:
Cybercriminals frequently use known weaknesses in outdated software. A regular patch ensures that well-known security holes are closed.
Best Practice: Apply updates and patches promptly—whether using SharePoint online or an on-premises version. Regular maintenance is a key component of modern security hygiene.
7. Control External Sharing:
External sharing allows users to work with people outside their organization, but it can also represent security risks if not properly managed.
Best Practice: Limit external sharing to specific files or sites and enable auditing to track what’s shared. These steps reinforce security protocols and mitigate risk.
8. Monitor and Respond to Security Alert:
Threats and security gaps occur constantly, and early detection is important in reducing potential risks.
Best Practice: Apply updates and patches promptly, whether using the online or on-premises versions. Regular maintenance is a key component of modern security hygiene.
Conclusion
Securing your SharePoint environment requires a proactive approach. Your team can mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive data by implementing best practices such as multi-factor authentication, regular permission audits, encryption, and continuous monitoring. As cyber threats continue to evolve, strong Microsoft SharePoint security isn’t optional, it’s what keeps your data safe, your organization compliant, and your operations running smoothly.
Master Security Management for Compliance & Protection
Partner with AlphaBOLD to align your SharePoint with regulations and safeguard your data from cyber threats.
Request a ConsultationExplore Recent Blog Posts