What is Social Engineering ?
Social engineering is an act of manipulating social situations and individuals into revealing sensitive data and personal information to use for illicit purposes. Hackers need the slightest “in” to an organization such as a password or perhaps a firewall rule to circumvent. Once a social engineer obtains the password of an employee, they can simply log in and snoop around for sensitive data. With your company access card or entrance code, a hacker can gain physical access to a facility, data centers or office where they can, harm assets or people
Types of Social Attacks
Below are a few common types of social attacks:
1: Phishing
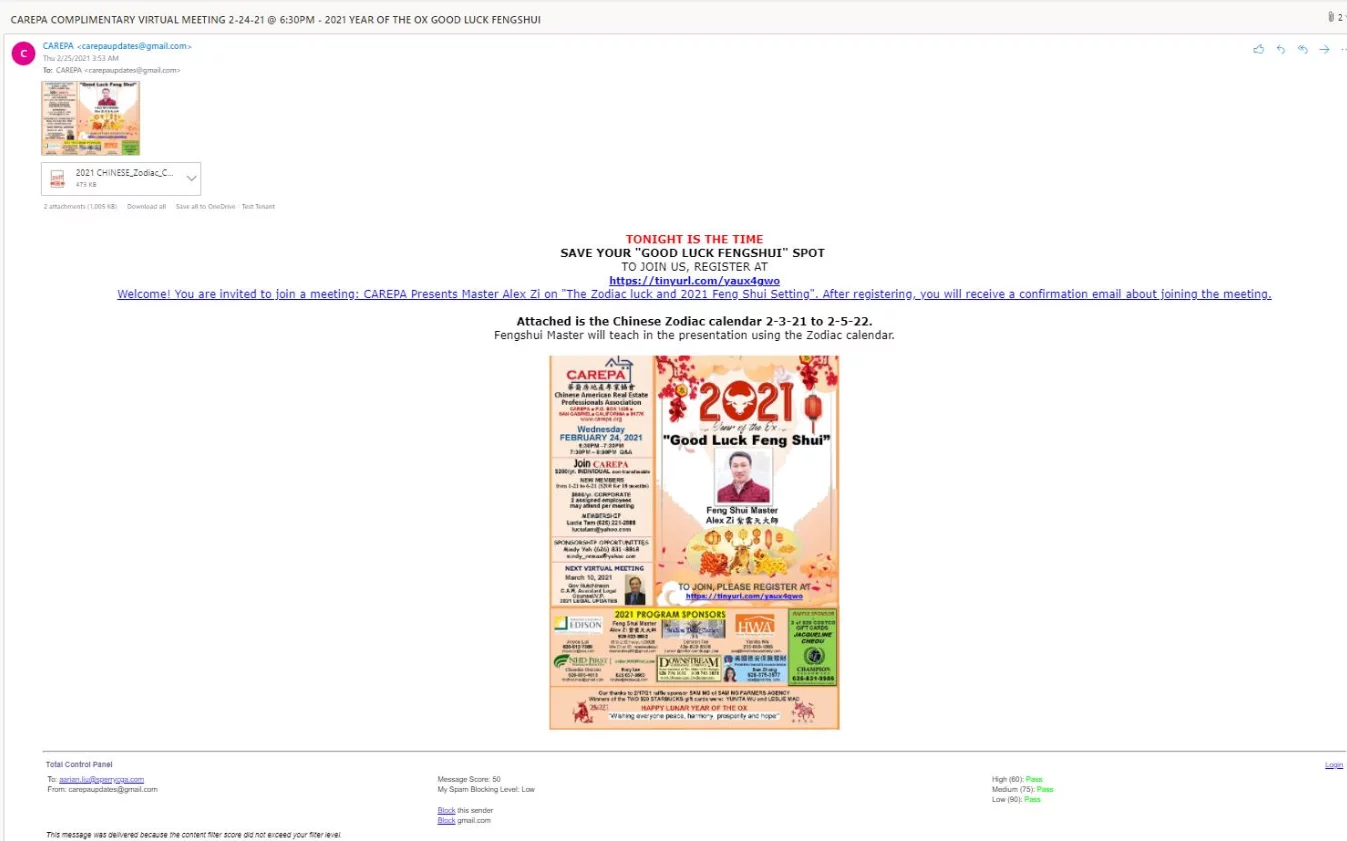
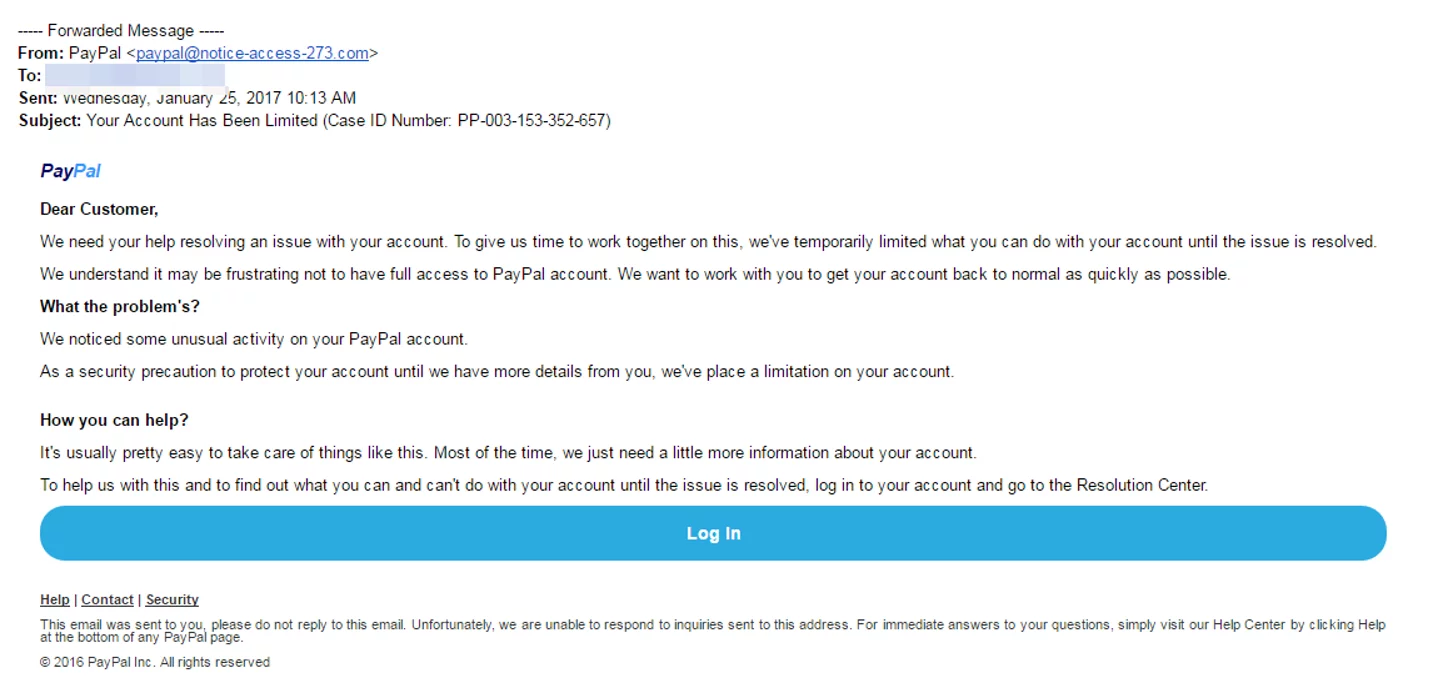
Phishing is one of the most common social engineering methods where the social engineer uses text, call, or email, pretending to be from a reputable company, institution, or organization, to trick the victim into revealing sensitive information.
For example, the attacker might send an email with a subject line: You will win the prize,” Open this link to see my images” or something else like this. When you click on the link, it takes you to a form that asks for your email or social networking site’s credentials. Once you give those details, your account gets hacked.
Following are some examples of phishing emails:
2: Cryptography
Cryptography is an old technique that’s been in use since 400BC. Cryptography is a way you can securely protect the data that you don’t want anyone else to access. It’s used to protect corporate secrets, secure classified information, and protect personal information from identity theft. Cryptography converts data into ciphertext.
Nowadays, hackers use these techniques for capturing wireless passwords and in some cases, they can crack your Windows or Linux passwords as well. Hackers may capture your wireless password and the password is in either hash form or in cipher text so they de-hash or decode using different Linux tools.
Basically, cryptography is an art of hiding data either in ciphertext or in encrypted text. We convert or encrypt our normal text into an unreadable form to protect it from other people. Cleartext is readable and understandable data, and ciphertext is scrambled text because of the encryption.
Data encryption provides confidentiality, meaning authorized users can only read the data. Message hashing provides integrity, which ensures that the receiver receives the same data as sent and the information is not modified during transmission. Message’s digital signatures further provide confidentiality, authentication (ensuring users are who they say they are), and integrity, along with message encrypting
3: Steganography
This is another social engineering technique where hackers bind or hide the object in an image or mp3 file. For example, the hacker can send you an anonymous script via text messages or a social media platform, attached with an image (maybe your image) or an audio file. It can harm your personal or official equipment as well.
This is one of the most dangerous techniques used by hackers because the script is hidden within the image, and it gets hard to judge whether it is a normal image or a deceptive one.
“Every dead system is a secure system.”
4: Homoglyph Attacks
In this technique, hackers trap the victim by using similar names/links.
Example: Here are two types of links: login.com and Iogin.com. Both links seem the same, but they are written with different spellings. In the first link, login.com is written with the small ‘L;’ whereas, in the second link, capital ‘I’ is used.
Just like the above-given example, hackers use similar but misspelled words in the URL to deceive the potential victims. Most of the time, this trick works!
Types of Hackers
The term hacker is usually associated with a person who breaks into the system to get personal data for fraudulent purposes. But not all hackers get unauthorized access to a computer system with a negative purpose. Hackers are basically categorized by the type of metaphorical hat they wear white hat, gray hat, and black hat. Hackers can be good or bad, depending on their hacking motives.
Different types of hackers, including the good and the bad ones:
Type # 1: Black Hat
A Black hat hacker uses and manipulates technology with vicious and often illegal intent. Simply put, they are the bad guy.
These shadowy figures are what come to mind when most people imagine the stereotypical hacker. Black hat hackers may be motivated by ill-gotten financial gains achieved by selling sensitive data or even simply for fame among fellow hackers.
Type # 2: White Hat
White hat hackers, also known as ethical hackers or penetration testers, are talented hackers employed by legitimate businesses or organizations to combat the efforts of malicious cyber security threats. In other words, they are the good guys. Their primary duties include purposely attempting to hack client systems, revealing discovered weaknesses, and reporting their findings to the proper authorities who employed for corrective action and risk management.
Type # 3: Gray Hat
A gray hat hacker frequently blurs the lines between black and white hat hackers. Gray hat hackers use their hacking talents much like white hat hackers do, yet without the host company’s permission. Once they discover cybersecurity weaknesses in various systems, they will offer to sell the information they have gathered to other hackers. Gray hat hackers are also known to use their skills in the whistleblower capacity to uncover unethical or illegal activities within the fabric of the organization. Though their methods of obtaining such information may itself be a tad questionable.
How to Protect Yourself?
Did you know there is a hacker attack every 39 seconds? It shows that social engineering has become a prevalent phenomenon in today’s IT landscape, and it’s becoming increasingly difficult to avoid these attacks.
With some know-how and understanding, you can still save yourself from social engineering. Here are some helpful tips:
Identifying social engineering emails
Social engineering attacks typically occur through an email, ad, or a website that looks like sites you already use. Social engineering emails look like they’re from a legitimate source, such as your bank, office, or from a colleague, but they are not.
Never send personal information through an email unless you are absolutely sure who is the receiver. Don’t use the URL address mentioned in the message since it can be forged (usually you can see the actual address of a URL by hovering over it). Legitimate sites, like social media sites or your bank, never send unsolicited messages asking for your password or financial details. If you are getting an email asking for this information, be suspicious and don’t download any attachments unless you are sure of their origin. If you have an IT department, ask them how they would like you to handle the reporting of such suspicious emails.
Avoiding social engineering attacks on the web
A website cannot tell you your machine is in danger.
- If the site says you have a security issue or infection and asks you to download software, don’t. You should only download software from a trusted source.Page Break
- Attackers will often make a URL look similar to a genuine site. Before entering your important information verify the link/URL uses HTTPS and that it a valid and trusted site. HTTPS is quite secure and encrypted.
Looking for browser warnings
Some browsers, like Firefox, Chrome, or Edge, will warn you if the site you are trying to visit is suspected of social engineering or malware. Get use to checking for these warnings.
Conclusion
A social engineering attack occurs when someone tries to trick you into their traps such as downloading software or sharing files like bill details etc. across internet.
The following tricks & tips may help you to protect yourself from hackers:
- Think before you click
- Research the sources
- Email spoofing is ubiquitous, so verify the sender
- Don’t download files from untrusted sources
- Don’t fall for offers and prizes messages
- Delete any request for demanding your personal information or passwords
- Set your spam filters to high
- Secure your devices
- Always be mindful of risks
- Only use HTTPS sites when submitting information.
After all:
“Safety starts with awareness; awareness starts with you.”